Transferable Metal Electrodes
-
Estimated Delivery:Mar 16 - Mar 20
Transferable Metal Electrodes
Introduction
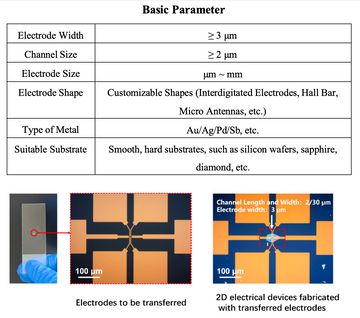
Two-dimensional materials offer promising avenues to advance Moore's Law. In recent years, the research on electrical devices based on these materials has gained considerable attention. When fabricating two-dimensional electrical devices, transferable metal electrodes can establish van der Waals contacts with two-dimensional materials through mechanical stacking. This approach effectively prevents damage caused by traditional micro/nano fabrication processes, thus improving device yield. Moreover, transferable metal electrodes provide a convenient, ready-to-use solution compatible with the transfer techniques commonly employed in two-dimensional material research. This enables rapid processing and fabrication, significantly enhancing the performance of two-dimensional electrical devices.
Instructions for Use
This process mirrors the techniques used in transferring two-dimensional materials:
1. Transfer: Utilize the transfer platform to precisely align and stack the transferable metal electrodes onto the target substrate (sample).
2. Adhesion: Heat the assembly to 150°C and maintain this temperature for 15 minutes to ensure a secure bond between the adhesive layer and the electrodes with the target substrate.
3. Peeling: While maintaining the temperature at 150°C, lift the glass slide with the electrodes. Use tweezers to carefully peel off the PDMS from the target substrate. Discontinue heating once the peeling process is complete.
4. Debonding: Remove the adhesive layer by soaking the assembly in acetone for five minutes. Alternatively, the adhesive layer can be left in place as a sealing layer.
Pro Tip: For optimal performance, we recommend annealing the device post-transfer to minimize contact resistance
We want you to be 100% satisfied with your purchase.We will ship in 2-3 weeks.












